Classification
Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF)
HFrEF is an EF less than or equal to 40%.
There is a mortality benefit proven with Carvedilol, long acting metoprolol (succinate), and bisoprolol, ACE inhibitors/ARBs, or spironolactone.
Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)
A clinical syndrome in which patients have symptoms and signs of HF, a normal or near normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF ≥50 percent), and evidence of cardiac dysfunction as a cause of symptoms (i.e. abnormal left ventricular filling and elevated filling pressures).
- Approximately 50% of patients with HF have an EF>50%, a proportion that is increasing over time and is the dominant form of HF in the elderly
- No therapies have a proven mortality benefit, unlike HFreF
HFpEF primary treatment focuses on maintaining euvolemia and effectively managing associated comorbidities.
Major disease focus areas: atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, diabetes, pulmonary hypertension, obesity, cardiac valvular disease, chronic anemia, and rheumatologic disease.
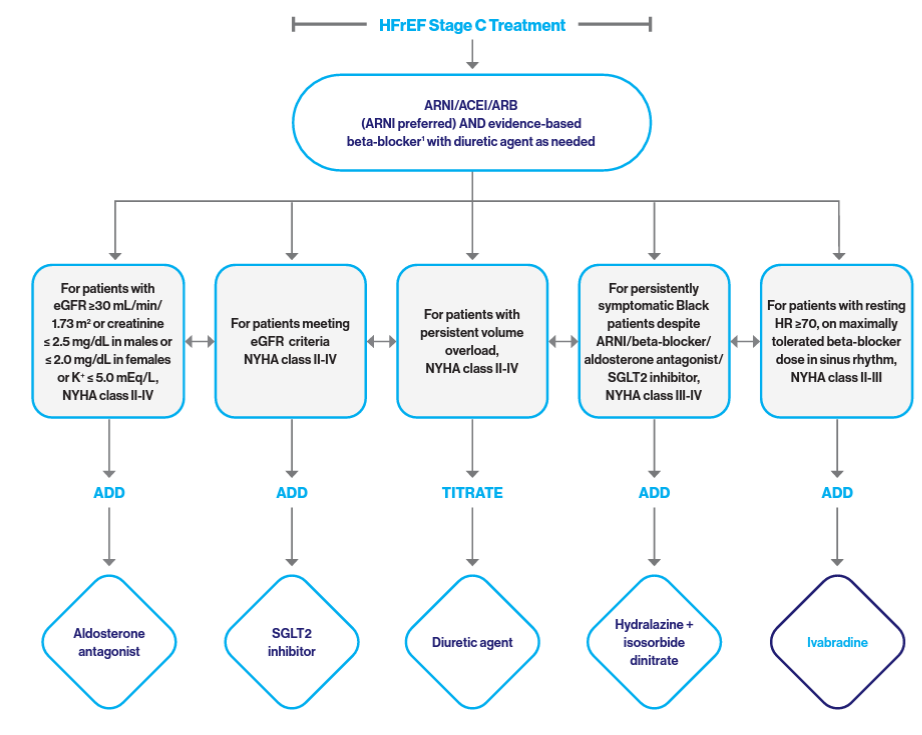
Treatment Algorithm for Guideline Directed Medical Therapy Including Novel Therapies

Pharmacology
Starting and Target Doses of Select Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy (GDMT) for HF
| Starting Dose | Target Dose | |
|---|---|---|
| ARNI | ||
| Sacubitril/valsartan | 24/26 mg-49/51 mg bid | 97/103 mg bid |
| ACEI | ||
| Captopril | 6.25 mg tid | 50 mg tid |
| Enalapril | 2.5 mg bid | 10-20 mg bid |
| Lisinopril | 2.5-5 mg qd | 20-40 mg qd |
| Ramipril | 1.25 mg qd | 10 mg qd |
| ARB | ||
| Candesartan | 4-8 mg qd | 32 mg qd |
| Losartan | 25-50 mg qd | 150 mg qd |
| Valsartan | 40 mg bid | 160 mg bid |
| Beta Blockers | ||
| Bisoprolol | 1.25 mg qd | 10 mg qd |
| Carvedilol | 3.125 mg bid | 25 mg bid for weight <85 kg; 50 mg bid for weight ≥ 85 kg |
| Metoprolol succinate* | 12.5-25 mg qd | 200 mg qd |
| Aldosterone Antagonists | ||
| Eplerenone | 25 mg qd | 50 mg qd |
| Spironolactone | 12.5-25 mg qd | 25-50 mg qd |
| Vasodilators | ||
| Hydralazine | 25 mg tid | 75 mg tid |
| Isosorbide dinitrate | 20 mg tid | 40 mg tid |
| Fixed-dose combination isosorbide dinitrate/hydralazine | 20 mg/37.5 mg (one tab) tid | 2 tabs tid |
| HCN Channel Blockers | ||
| Ivabradine | 2.5-5 mg bid | Titrate to HR 50-60 bpm; max dose 7.5 mg bid |
| Loop Diuretics | ||
| Bumetanide | 0.5-1 mg qd or bid | 10 mg qd |
| Furosemide | 20-40 mg qd or bid | 400 mg qd |
| Torsemide | 10-20 mg qd | 200 mg qd |
| Cardiac Glycosides | ||
| Digoxin | 0.125 mg qd | 0.25 mg qd |
| SGLT2 Inhibitors | ||
| Dapagliflozin | 10 mg qd | 10 mg qd |
| Empagliflozin | 10 mg qd | 10 mg qd |
*Unlike immediate-release metoprolol and atenolol, metoprolol ER is proven to improve symptoms of heart failure, lower the risk of death from heart failure, and lower the risk of hospitalization due to heart problems. While atenolol is technically another hypertension drug, it doesn’t have these additional benefits.
! Medications to Avoid in HF
- NSAIDs in all types of HF
- Second generation calcium channel blockers such as amlodopine may be used for blood pressure control in HFrEF
- Other calcium channel blockers such as verapamil, diltiazem, and nifedipine should be avoided in patients with HFrEF
- Nitrates in HFpEF
New Therapies for HFrEF: SGLT-2i (Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors)
Canagliflozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), and Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
Consider adding a SGLT2 Inhibitor if GFR >30 in the following groups of patients:
- Patients with and without diabetes
- Patients with HFrEF
- Patients with worsening CKD (step 4 if still symptomatic on ARNI, B-Blocker, Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist)
HFpEF BNP considerations
- Absolute values are lower than in HFpEF, with up to 30% of HFpEF patients having normal levels
Ischemic Evaluation
Noninvasive cardiac imaging is indicated to detect myocardial ischemia and viability in HFrEF and HFpEF patients with known or suspected CAD. Cardiac catheterization should be considered for patients with significant CAD who would be candidates for revascularization (PCI or CABG).
When to Refer
Consider referring the patient to specialty care in the below cases.
Newly-onset HF (regardless of ejection fraction)
Refer for evaluation of etiology, guideline-directed evaluation and management of recommended therapies, and assistance in disease management, including consideration of advanced imaging, endomyocardial biopsy, or genetic testing for primary evaluation of newly-onset HF.
Chronic HF with high-risk features
Development of one or more of the following risk factors:
- Need for chronic IV inotropes
- Persistent NYHA functional class III-IV symptoms
- Systolic blood pressure ≤90 mm Hg or symptomatic hypotension
- Creatinine ≥1.8 mg/dl or BUN ≥43 mg/dl
- Onset of atrial fibrillation, ventricular arrhythmias, or repetitive ICD shocks
- Two or more ED visits or hospitalizations for worsening HF in prior 12 months
- Inability to tolerate Guideline Directed Medical Therapy (GDMT)
- Clinical worsening
Other Indications
- To assist with management of GDMT, including replacement of ACEI or ARB therapy with ARNI for eligible patients or to address comorbid conditions
- Annual review for patients with established advanced HF
- Persistent reduced LVEF ≤35% despite GDMT for ≥3 months for consideration of device therapy in those patients without prior placement of ICD or CRT, unless therapy is contraindicated
Device Therapy
- Consider EP referral for primary ICD or CRT in patients with EF ≤35% for at least 90 days (or 40 days post MI) on chronic GDMT
Cardiac Rehab
- People of all ages with heart conditions, including HF, can benefit from a cardiac rehab program
- Medicare and most other insurers provide reimbursement for cardiac rehab for HFrEF
Locations
| Hospital | Address | Phone |
|---|---|---|
| Mount Sinai Doctors – East 85th Street | 234 E 85th Street, Lower Level, New York, NY 10028 | 212-241-8597 |
| Mount Sinai South Nassau | 440 Merrick Road, Oceanside, NY 11572 | 516-255-8280 |
Vaccinations
| Influenza vaccine | Recommended for all patients with HF |
|---|---|
| Pneumococcal vaccination | The PPSV23 is recommended for all adult patients with heart failure. Administration of PCV13 should also be considered for patients ≥65 years old. |
Team-Based Care
Leverage the support of additional care team members to effective manage patients with chronic conditions. Available services include:
- Clinical pharmacists
- Certified Diabetes Educators (CDE/Wellness Coaches)
- Care management
- Behavioral health
- Palliative care
Next Steps
- Review the MSHS Ambulatory Care Pathway for Heart Failure for more in-depth guidance on evidence-based best practices
- Print and share resources with your patients to empower them to meet their care goals
- Check out our past Heart Failure Condition Management Tips for quick takeaways to keep you up-to-date on management guidelines
