Chronic Kidney Disease Quick Guide
Managing CKD in your primary care practice? Find resources to help you. Follow this handy checklist to ensure you complete your screenings and meet clinical targets, review diagnosis and staging criteria as well as common medications in CKD, gain confidence in managing complications and comorbidities, and know when to refer to a specialist.
Download a print-friendly PDF of this page
Checklist for CKD Management for Frontline Providers
|
Screening/Management |
Clinical Targets |
Frequency of Testing/Visits |
Next Steps for Uncontrolled/Positive Finding |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Estimate GFR and Albuminuria |
GFR >=90 Urine ACR <30 mg/g |
Stages 1-2: Annually Stage 3: Semiannual Stages 4/5: Quarterly |
Determine if progressive Estimate risk for progression (Kidney Failure Risk Equation or KidneyIntelX in diabetics) |
|
Nutrition |
Protein Intake Stage 5: 0.6-0.8 g/kg/d Sodium intake Stages 3/4-5: <4g/3 g/d Stages 3-5 w Htn: <2 g/d |
Annually and as needed |
Provide dietary counseling (Nutritionist or CDE) Protein composition recommended: 50% High Biologic Value and 50% plant-based |
|
Blood Pressure Control |
Target Blood Pressure: <130/80 |
Monthly until controlled, then every 3-6 months |
Lifestyle modification, Home BP monitoring Non-Diabetic: ACR <30 mg/g, GFR <60: Use ACE/ARB, CCB, Diuretic ACR 30-299 mg/g: Use of ACE/ARB suggested ACR >300 mg/d: Use ACE/ARB Diabetic: ACR<30: Use ACE/ARB, CCB, and/or Diuretic ACR >30 or GFR<60: Use ACE/ARBR |
|
Diabetes Mellitus Management |
HbA1c <7% (range <6.5-8%) Urine ACR <30 mg/g |
Controlled: q 6 mon Poorly controlled: q 3 mon |
Intensify medications to optimize control With CKD, both metformin and SGLT-2i as first line therapy Use GLP-1 RA if intolerant to SGLT-2i or GFR <30 |
|
Lipid Management |
LDL <130 or <100 based on ASCVD risk |
Annually |
Lifestyle modification Statin therapy for Stage 3-5 (Non-Dialysis) |
|
Metabolic Acidosis |
Sodium Bicarbonate >22 meq/l |
Stage 1-2: Annual Stage 3: q 6 mon Stages 4/5: q 3 mon |
If bicarbonate <22 mEq/l, add sodium bicarbonate (650 mg TID) or sodium citrate (30 ml/d |
|
Anemia |
Hgb level >13 mg/dl men, >12 women |
Stage 3: Annual Stages 4-5:q 3 mon On ESA : q 3 mon |
Replete iron orally or IV if iron deficient (FeS04 325 mg TID, Fe gluconate 2-3 mg/kg/d BID-TID) Erythropoiesis Stimulating Agents if refractory |
|
Bone Metabolic Disease |
Normal Calcium and Phopshate concentrations |
Screening at GFR <5 Stage 3B: q 6-12mon Stage 4: q 3-6 mon Stage 5: q 1-3 mon |
Correct hypocalcemia if <7.5 mg/dl (adjust-ed for albumen), symptomatic, or severe hyperPTH Treat hyperphosphatemia with diet (~900 mg/d) and phosphate binders if >6 mg/dl |
|
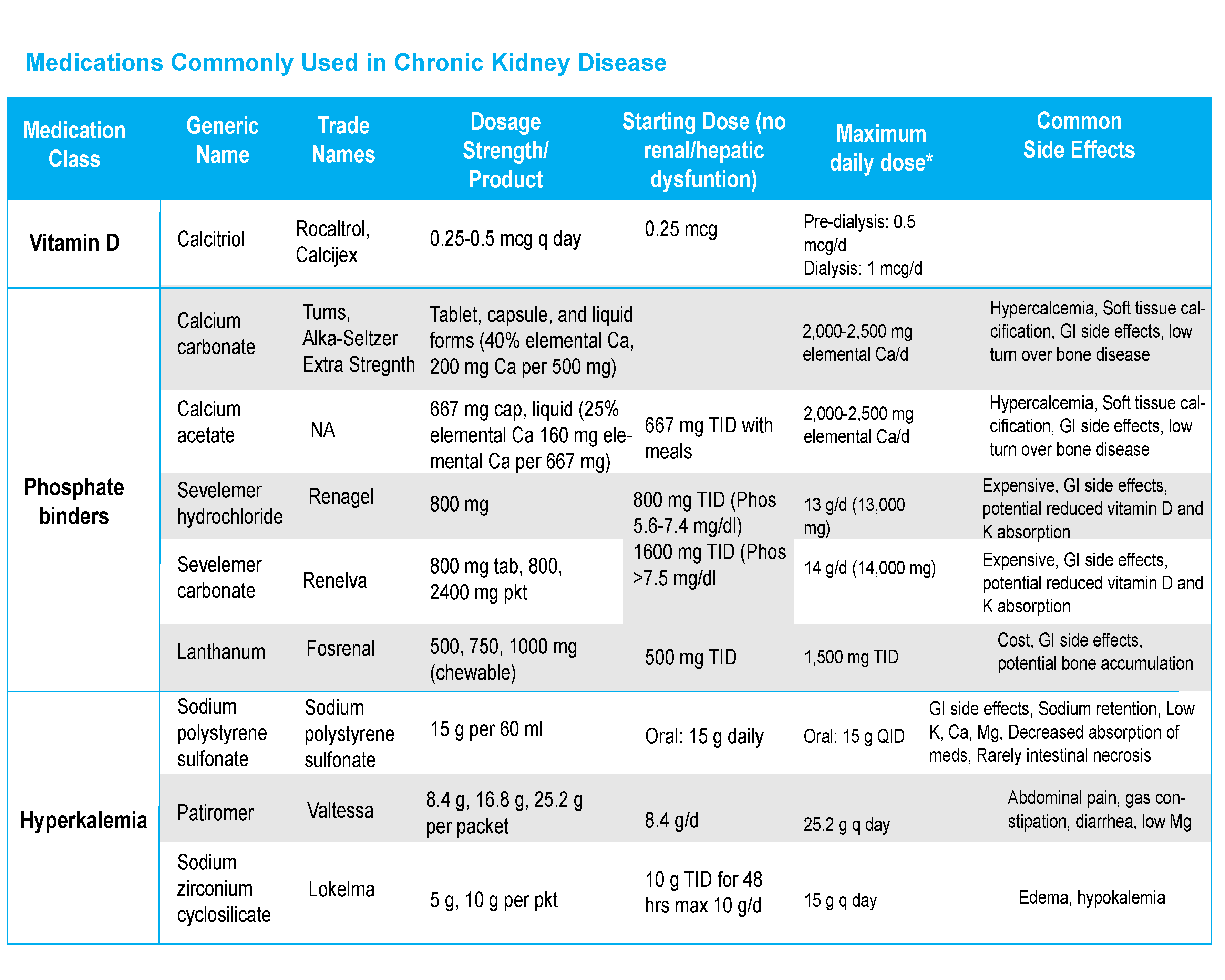
Vitamin D |
Screening to establish baseline and as needed |
Correct as without CKD, if Phosp/calcium normal. Calcitriol or synthetic vitamin D analogs if progressive hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
Parathyroid hormone level |
Stage 3B: Baseline Stage 4: q 6-12 monStage 5: q 3-6 mon |
Correct modifiable factors Calcitriol/Vit D analogues for severe progressive disease |
|
|
Hyperkalemia |
Serum Potassium |
Stage 1-2: Annual Stage 3: q 6 mon Stages 4/5: q 3 mon |
Low potassium diet Reduce or eliminate contributing meds Correct acidosis Sodium polystyrene, Patiromer, or Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate |
|
Behavioral Health |
Depression Screen: PHQ 2/9 |
Annual Screening |
Confirm diagnosis of depression Initiate treatment and/or refer |
|
Immunizations |
PPSV23 Hepatitis B Influenza |
1x if GFR <30 or higher risk, repeat in 5y. Complete Hep B series when GFR <30 and at risk of progression. Annual influenza vaccination. |
Consider administration of PV 13 at 65yrs Check HepBs Ab to confirm immunity |
Diagnosis & Staging
History: majority of cases are asymptomatic and detected incidentally or through screening
• Chronic kidney disease is defined as any abnormality of kidney function or structure lasting at least 90 days
• CKD should be distinguished from acute kidney injury (2-7 days) and acute kidney disease (<3 months)
Diagnostic Testing
• Estimate GFR using serum creatinine, age, gender (typically on lab report, do not adjust by race)
• Measure urinary albumin excretion: urine albumin to creatine ratio (ACR) preferred test
• NOTE: In Epic, “Kidney Profile” order includes eGFR, urine albumin, and urine creatinine.
• Renal ultrasound typically obtained to assess kidney structure and rule out obstruction.
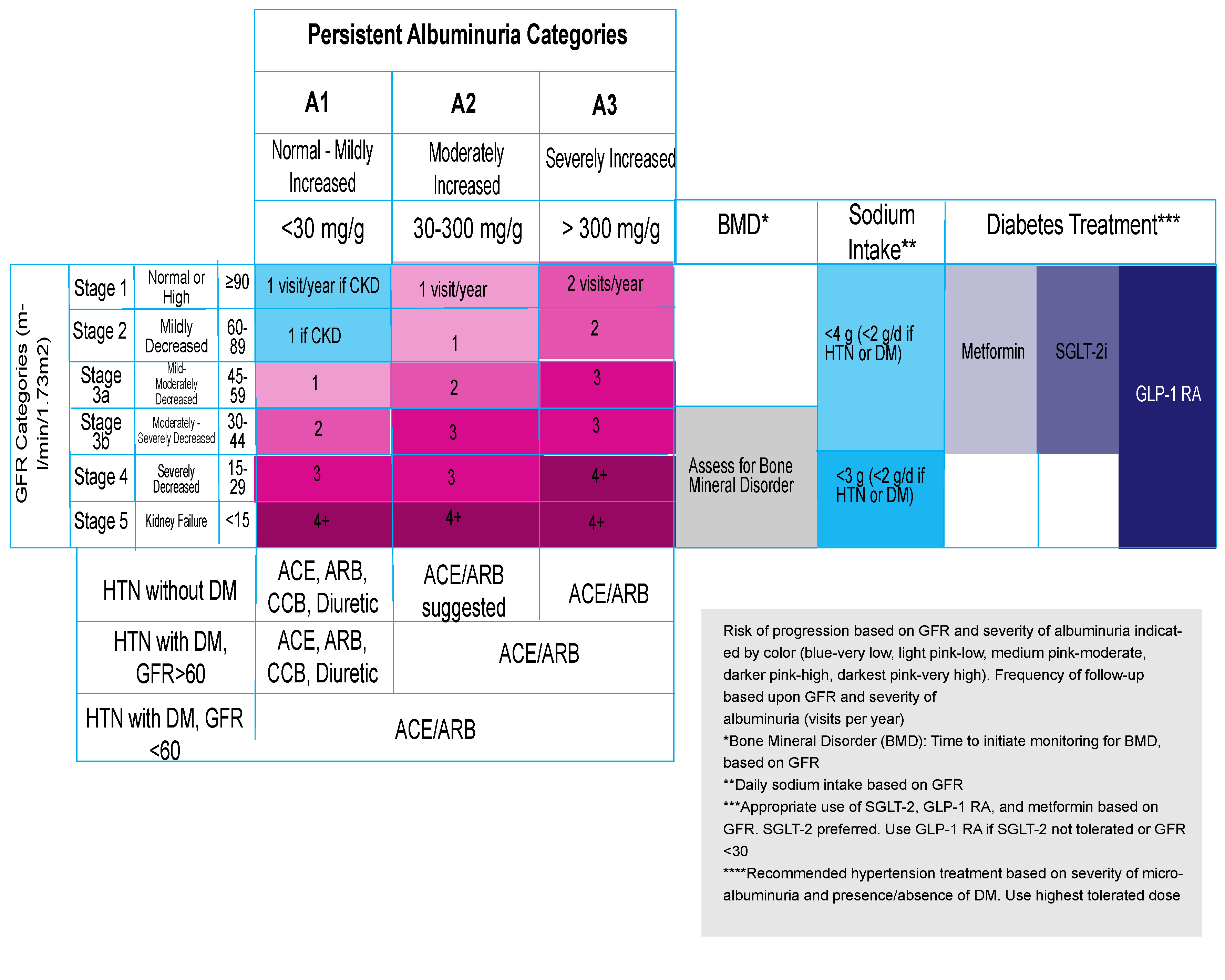
Classification - focus on GFR AND level of albuminuria
• Stratify GFR into Stages 1-5, urine ACR into stages A1-A3
• Use table below to classify risk of progression, monitoring frequency, and time interventions
• Progression defined as drop in GFR category and a 25% decrease from GFR baseline
• Rapid progression is a decline in GFR of = 5 ml/min/1.73m2 per year
• If GFR <60, use Kidney Failure Risk Equation to estimate 2 yr and 5 yr of dialysis or renal transplantion (https://kidneyfailurerisk.com/) or KidneyIntelX for diabetic
Diet & Lifestyle
|
Component |
CKD Status |
Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
|
Protein |
Stage 5 (Possibly Stages 3b-4) |
Consider 0.6-0.8 g/kg/d protein (50% high biologic value, 50% plant based) (70 kg pt =70g, ¼ pound of beef or cheese has 28 g protein, ½ cup grain has 3 g) |
|
Salt |
Stage 3-5 |
<4 g/d Stage 3, or <;3 g/d for Stage 4-5, symptomatic fluid retention/proteinuria, <2g/d if hypertensive or diabet-ic (1/4 teaspoon salt has 575 g sodium) |
|
Potassium |
Stage 3 |
<4.7 grams per day (442 mg per banana, 230 mg in ¼ cup orange juice) |
|
Stage 4-5 |
<3 grams per day |
|
|
Calcium |
Stage 3-5 (Pre-dialysis) |
800-1,000 mg daily (1 calcium carbonate tablet has 500-600 mg elemental Ca) |
|
Fluids |
Stage 3 |
Restrict to <1.5 liters per day (approximately six 8 oz glasses of water) |
|
Energy |
All |
30-35 kcal/kg per day |
|
Exercise |
All |
30 minutes a day, five days a week |
Delaying Disease Progression
Hypertension
Diabetes Mellitus
Screening
-
Annual urine ACR and GFR estimation, start 5 yrs after dx of DM1, upon dx of DM2
Type 2 DM Treatment Recommendations (see table)
-
Target HbA1c: Range 6.5%-8% depending on comorbidities, life expectancy, CKD severity
-
Use SGLT-2 inhibitor with metformin if GFR >30, and UACR >30 mg/g, particularly if UACR >300 mg/g
-
Use GLP-2 RA if SGLT-2i contraindicated (GFR <30), not tolerated or 3rd antihyperglycemic needed
Managing Complications
Metabolic Acidsosis (See Table)
-
If HC03 <22 mEq/l: treat with oral bicarbonate to normalize level
Hyperkalemia (See Table)
-
Severe (K> 6.0—6.5 mEq/l): clinical emergency mandating immediate care
Iron Deficiency Anemia
-
Iron supplementation useful in both absolute and functional iron deficiency
Bone Mineral Disorder
-
Hypocalcemia: Supplement calcium if severe, progressive secondary hyperparathyroidism, not if mild
-
Vitamin D Deficiency
-
Calcitriol use limited to progressive hyperparathyroidism (PTH levels 2.5-3X upper limit of nml)
-
Calcitriol 0.25 mg three times a week, if corrected Ca <9.5 and normal phosphate
-
Non-calcium containing binders
-
Other synthetic vitamin D agents
-
Managing Common Comorbidities
Cardiovascular Disease
Coronary Artery Disease: Antiplatelet Therapy
• Primary Prevention: ASA/other antiplatelet agents may be modestly useful
• Secondary Prevention: Low dose ASA (81 mg) is preferred to higher doses
Heart Failure
• SGLT-2 inhibitors have beneficial effects on HF and CKD, with and without DM
Lipid Disorders
• Treatment recommendations for patients 40-75 years old
• Patients with GFR 15-60 and/or urine ACR >30 mg/g not receiving dialysis or post-transplant with 10 yr ASVCD risk >7.5% should be treated with a statin +/- ezetimbi
• GFR >60 and albuminuria or other kidney disease, should receive a statin or have treatment reserved for those with increased ASCVD risk
• Moderate intensity statin doses recommended (e.g. Atorvastatin 40 mg/d), unless other indications for high dose. Doses of renally excreted statins may need to be reduced.
Clinical Integration Care Delivery Steps
Nephrology Referral Indications
• Clarify cause of CKD and/or assistance managing related complications, AKI or abrupt sustained fall in GFR.
• All Stage 4-5 CKD (GFR <30), urine ACR >300 mg/g, KidneyIntelXTM medium or high risk score
• Resistent hypertension, persistent hyper-/hypokalemia, hyperphosphatemia, anemia warranting ESA
• Planning for or initiation of dialysis (if risk of kidney failure within next year is >10-20%) • Transplantation: Should be considered if GFR <20 with likely progressive, irreversible CKD over next 6-12 months
Find a nephrologist
Care Management Referral Indications
• Multiple no-shows, treatment non-adherence• Demonstrated difficulty managing symptoms and/or disease processes
• Frequent potentially preventable admissions or ED visits
• Complex family dynamics, difficulty accessing needed community-based care, and/or a high “worry score”
Use MSHP Care Management Referral in Epic, email mshpcmreferral@mountsinai.org, or call 212-241-7228
Prefer to print this page? Download a PDF version.
References
1. Chen TK, Knicely DH, Grams ME, Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Man-agement: A Review. JAMA. 2019 October 01; 322(13): 1294–1304
2. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease Kidney International Supplements 2020;98:1-120
3. KDIGO 2017 Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Kidney International Supplements, 2017;7:1-